Map 集合介绍
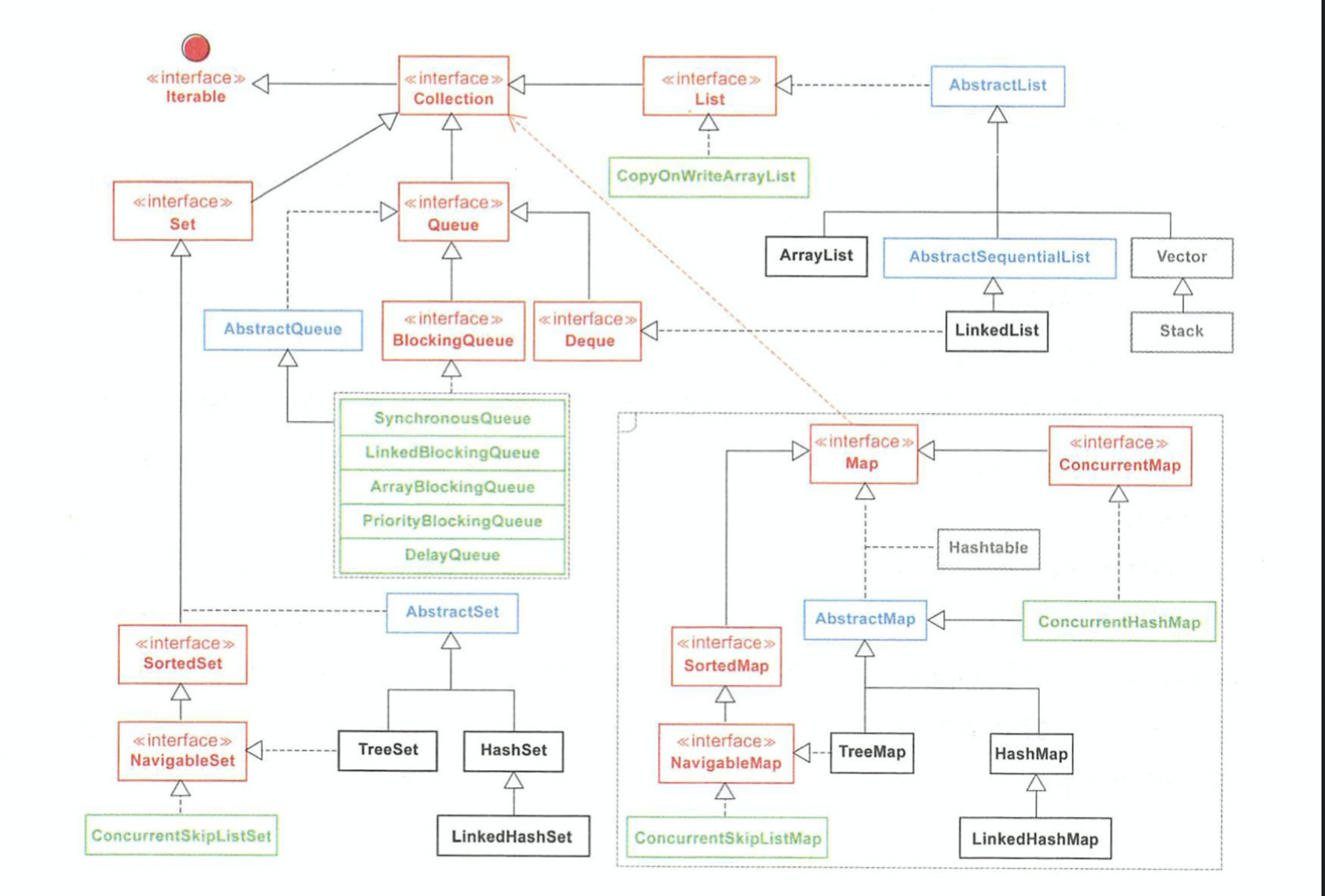
Map 集合是以 Key-Value 键值对作为存储元素实现的哈希结构,Key 按某种哈希函数计算后是唯一的,Value 则是可以重复的。 常用的 Map 集合主要有 HashMap 和 TreeMap 这两个类。
HashMap 集合介绍
HashMap 是基于哈希表的数据结构实现的(数组+链表),无序,Value 值可以重复,可以存入null键和null值,线程不同步不安全,效率较高。
哈希表:根据关键码值(Key value)直接进行访问的数据结构。通过把关键码值映射到表中一个位置来访问记录,以加快查找的速度。这个映射函数叫做哈希函数,存放记录的数组就叫做哈希表。
HashMap 组成
HashMap 是基于哈希表的数据结构实现的(数组+链表)。两个重要的属性:加载因子(loadFactor)和边界值(threshold)。底层源码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
|
HashMap Put 方法介绍
初始化完成后,HashMap 就可以使用 put() 方法添加键值对了。从下面源码可以看出,当程序将一个 key-value 对添加到 HashMap 中,程序首先会根据该 key 的 hashCode() 返回值,再通过 hash() 方法计算出 hash 值,再通过 putVal 方法中的 (n - 1) & hash 决定该 Node 的存储位置。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1)
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
|
HasnMap 线程不安去
HashMap线程不安全,它的线程不安全主要发生在put等对HashEntry有直接写操作的地方,从put操作的源码不难看出,线程不安全主要可能发生在这两个地方:
- key已经存在,需要修改HashEntry对应的value。
- key不存在,在HashEntry中做插入。
解决方法:
- 可以用 Collections的synchronizedMap方法。
- 使用ConcurrentHashMap类,相较于HashTable锁住的是对象整体, ConcurrentHashMap基于lock实现锁分段技术。首先将Map存放的数据分成一段一段的存储方式,然后给每一段数据分配一把锁,当一个线程占用锁访问其中一个段的数据时,其他段的数据也能被其他线程访问。
TreeMap 集合介绍
TreeMap 底层结构是红黑树,有序,具体顺序可以由指定的 Comparator 来决定,或者根据键的自然顺序来判断,默认是升序排序。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| public V put(K key, V value) {
Entry<K,V> t = root;
if (t == null) {
compare(key, key);
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
int cmp;
Entry<K,V> parent;
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
do {
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
else {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else
parent.right = e;
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
}
|
